The coordinates latitude and longitude are used to plot and find specific locations on the Earth. Anyone can use the printable World Map with Latitude and Longitude to determine the precise location of a place by utilizing its latitude and longitude. The World Map with Latitude and Longitude can also suggest a country’s time zone.
The equator is at 0°, and the latitude is in degrees. To the north of the equator, the Northern space reaches 90 degrees, while to the south, the Southern margin reaches 90 degrees. Longitude is an angle measured from the Greenwich Meridian that points west or east. If the Prime Meridian is the Greenwich Meridian, the maximum longitude is 180 degrees east of the Prime Meridian and 180 degrees west of the Prime Meridian. On the world map with latitude and longitude, the coordinates refer to angles measured in degrees: minutes of arc and seconds of arc. 60 minutes of arc = 1 degree 60 seconds of arc = 1 minute
You may correctly discover the exact position of any site on the world using the latitude and longitude world Map. You can also check out the following maps:
Table of Contents
World Map with Latitude and Longitude
Map of World with Latitude and Longitude
World Map with Latitude
What is Latitude?
World Map with Longitude
What is longitude?
The location of the Equator
Tropic of Cancer
Tropic of Capricorn
Locations of the Arctic and Antarctic Circles
Location of the Horse’s Latitudes
Meridians
How to Figure Out Whether a Meridian Is East or West
Distance between lines of longitude?
The Prime Meridian and what it means
The International Date Line and how it works
World Map with Latitude and Longitude
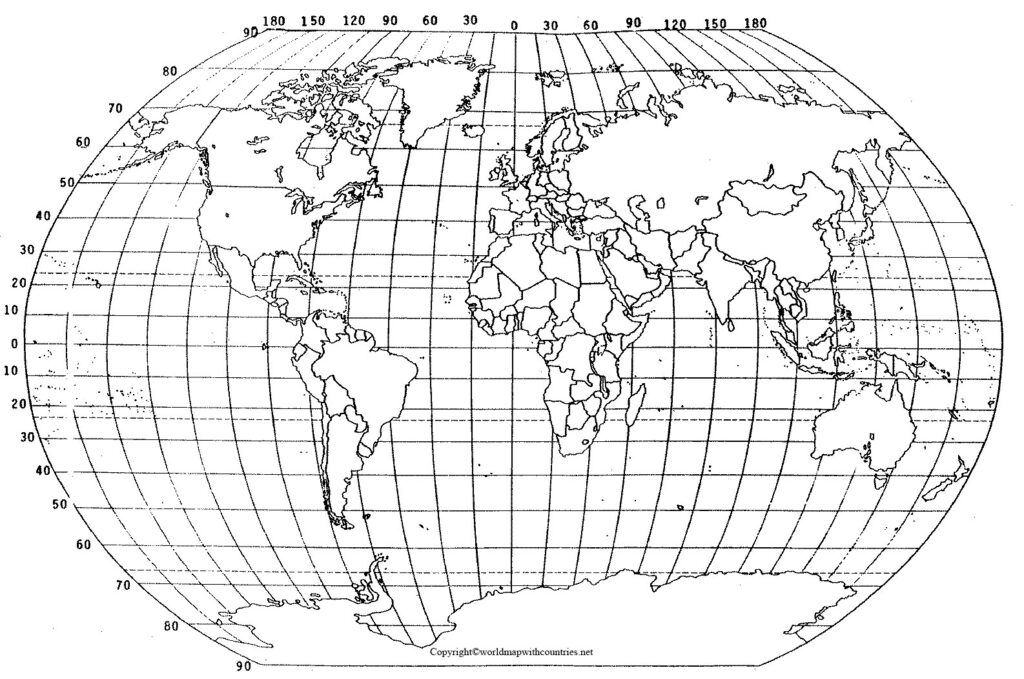
A World map with latitude and longitude will help you locate and understand the imaginary lines forming across the globe. Longitudes are the vertical curved lines on both sides and curves facing the Prime Meridian; these lines intersect at the north and south poles. Latitudes are the horizontal straight line around the globe on both sides of the equator.
By drawing latitudes and longitudes all over the globe, there is the formation of a grid which is helpful to find out the position of any location referring to the equator and prime meridian. For example, a point described as 50° N, 20° W, for example, is located 50° of arc north of the Equator and 20° of arc west of the Greenwich meridian.
The framework formed with the combination of latitudes and longitudes helps us to locate the position of any place geographically. The locations anywhere all around the globe, east, west, north, and south, can be easily found and described with the help of this formed grid.
The physical world map latitude and longitude, centered on Europe and Africa, depicts all continents, sovereign nations, dependencies, oceans, seas, oversized islands, island groups, countries with international borders, and their capital cities at 30° intervals. You can use the above map for educational or similar purposes.
Map of World with Latitude and Longitude
Latitudes and longitudes are helpful in earth geographical coordination and measure the distance of any particular location from the center of the earth. Degrees (°) and minutes (′) are the two scales of measurement used. The Equator lies at the 0° latitude; meanwhile, the prime meridian lies the 0°. From the prime meridian moving towards east or west, the location varies from 0° to 180°. We can also use Greenwich for 0° longitude, i.e., Prime Meridian. The map of the world with latitude and longitude will help you to know more about locations on the Earth.
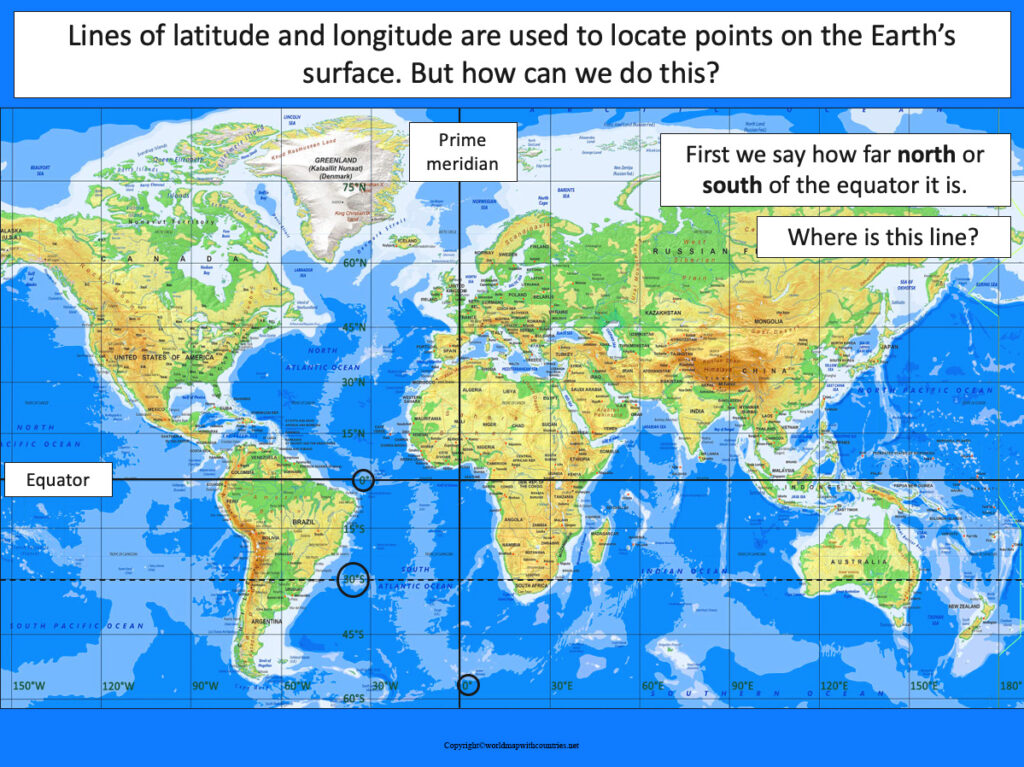
World Map with Latitude
Latitudes help measure the North and south positions of any location on both sides of the equator. Geocentric, astronomical, and geographic are the three kinds of plays. The most significant possible margin is 90° north to 90° south as all spaces parallel the equator. These latitudes are from Tropical climate zones, south polar regions and north polar regions. The World Map with Latitude shows this.
What is Latitude?
Parallels, often known as lines of latitude, are imaginary lines that split the Earth. They run east to west, but you can use them to calculate your distance north or south. The most well-known parallel is the equator. It splits the Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres equally at 0 degrees latitude. As you travel north or south from the equator, latitude increases, reaching 90 degrees at each pole. Other named lines of latitude exist. They assist us in comprehending climate, weather, and ocean currents because they’re based on the sun’s location during Earth’s orbit. The Tropic of Cancer, located at around 23 degrees north, and the Tropic of Capricorn, located at roughly 23 degrees south, define the tropics. The Arctic and Antarctic Circles are at approximately 66 degrees north and south, respectively. They restrict the Arctic and Antarctic areas. Check out the world latitude and longitude map to see all these.
On the Earth’s surface, each degree of latitude covers around 111 kilometers. One degree of freedom is divided into 60 minutes and one minute into 60 seconds. Only roughly 30.7 meters is covered by a second of play. Latitude lines are parallel, unlike longitude lines, which get closer to one other at the poles. Latitude lines are the same distance apart no matter where you are on the planet.
Since ancient times, latitude and longitude have been helpful in astronomy and navigation. Using simple equipment, navigators could calculate their approximate margin by calculating the angle between the horizon and a celestial object (typically the sun or the North Star). Because the calculations were straightforward, it took hundreds of years to determine accurate longitude readings at sea. The observer was in 60 degrees latitude if the North Star was 60 degrees above the horizon (north). In the southern hemisphere, where the North Star is not visible, the technique was more complicated.
We still use the sky to establish our location, but the technology is more advanced. Over 30 global positioning satellites orbit the Earth, delivering signals to land-based receivers. Over 30 global positioning satellites orbit the Earth, providing calls to land-based receivers. The National Geodetic Survey of the NOS oversees a network of Continuously Operating Reference Stations, which are stationary global positioning satellite receivers (CORS). Processed CORS data, when paired with additional positioning data from the National Spatial Reference System, can offer latitude, longitude, and height positions that are accurate to a few millimeters.
World Map with Longitude
Longitude is very important in measuring and determining positions on the world Map. The measurement of the Prime meridian east or west is one with the help of longitude at the Greenwich. These imaginary lines pass from one point at both poles and a middle line (prime meridian) from the Greenwich of London, Uk. On both sides of the prime meridian, east and west are measured up to 180°. These lines intersect the equator at the right angle (90°) and farthest at the equator and the poles. The World Map with Longitude shows this.
What is longitude?
The measurement east or west of the prime meridian is known as longitude. Longitude is determined by imaginary lines that go vertically (up and down) around the Earth and meet at the North and South Poles. Meridians are the names given to these lines. Each meridian measures one arc degree of longitude. The circumference of the Earth is 360 degrees. The sequence of 0 degrees longitude, or prime meridian, travels through Greenwich, England, is universally recognized. At 180 degrees, the antemeridian is halfway around the planet. The International Date Line is based on it.
The Eastern Hemisphere, or half of the globe, is measured in degrees east of the prime meridian. The Western Hemisphere, on the other hand, is located degrees west of the prime meridian. Sixty minutes are divided into degrees of longitude. Longitude can be divided into 60 seconds for each minute. The longitude of Paris, France, for example, is 2° 29′ E. (2 degrees, 29 minutes east). Brasilia, Brazil’s longitude is 47° 55′ W. (47 degrees, 55 minutes west). At its broadest point, a degree of longitude is around 111 kilometers (69 miles). Near the Equator, where the Earth bulges out, the most extended stretches of longitude are the most extensive. The actual distance of degrees, minutes, and seconds of longitude depends on the distance from the Equator due to the Earth’s curvature. The shorter the gap between meridians, the larger the space. At the North and South Poles, all meridians meet.
The measurement of distance north or south of the Equator is related to longitude. Parallels are latitude lines that run parallel to each other. Parallels and meridians are frequently used to create a grid on maps. A coordinate is a location on the grid where parallels and meridians intersect. We can use Coordinates to find any place on the planet.
For military, engineering, and rescue operations, knowing the exact coordinates of a site (degrees, minutes, and seconds of longitude and latitude) is essential. Military authorities can use coordinates to determine where weapons or opposing forces are. Engineers use coordinates to determine the optimal location for a building, bridge, well, or other structure. Coordinates assist pilots in landing flights or delivering humanitarian shipments to precise spots.
The location of the Equator
Check the world map with latitude and longitude to see where the equator splits the planet into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, where 0 degrees latitude is found. The angular distance north or south of the equator is represented by space. The equator denotes the point on the globe equidistant from both the North and South Poles. The Equator is the only latitude line with a large circle; all other latitude lines are tiny circles. The equator is around 24,901 miles (40,075 km) long and crosses 78.7% sea and 21.3 percent land.
Tropic of Cancer
In the World map with latitude and longitude, you will be able to see the tropic of cancer. At this latitude, the Tropic of Cancer denotes where the sun reaches its zenith. The precise play is not known. However, the most recent measurement for 2014 was 23° 26′ 14.675′′ (23° 26′ 16′′). The summer solstice, which occurs on June 20 or 21, is the day when the sun shines vertically above this parallel.
Tropic of Capricorn
The Tropic of Capricorn is a parallel line of latitude on the world map with latitude and longitude that moves every year and is currently placed at 23° 26′ 14.440′′. The winter solstice, which falls on December 21 or 22, each year, is the day when the sun shines vertically across this line.
Locations of the Arctic and Antarctic Circles
In the latitude and longitude world map, the Arctic and Antarctic Circles are around 66.5 degrees (66° 33′ 44′′ (or 66.5622°) latitude parallels. The Arctic refers to the area above the Arctic Circle, including the North Pole. The Antarctic is the territory south of the Antarctic Circle, consisting of the South Pole.
Location of the Horse’s Latitudes
Around 30 degrees north and south of the equator are the Horse Latitudes. The horse latitude zones in the subtropics where the prevailing winds divide and flow towards the poles (known as westerlies) or the Equator (known as equatorial winds) (known as trade winds).
Meridians
While we use parallels to describe lines of latitude, meridians are used to represent sequences of longitude.
How to Figure Out Whether a Meridian Is East or West
Distances west of the Prime Meridian are denoted by a – (negative values), whereas lengths east of the Prime Meridian are represented by a + (positive numbers) (-180 degrees of longitude west and 180 degrees of longitude east).
Distance between lines of longitude?
As you get closer to the equator, the distance between longitudes narrows. The distance between each line of longitude gets smaller as you get closer to the poles until they converge at the North and South Poles. At the equator, the distance between longitudes is the same as between latitudes, around 69 miles. The distance between them at 45 degrees north or south is about 49 miles (79 km). As the meridian lines converge at the poles, the distance between longitudes reaches zero.
The Prime Meridian and what it means
The Prime Meridian is the line of longitude where the degree is zero. It is also known as the Greenwich Meridian. It passes through the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, England, and divides the Earth into two halves, the Eastern Hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere.
The International Date Line and how it works
The International Date Line is a line on Earth that marks the transition from one calendar day to the next (IDL). The bar is usually found 180 degrees from the Prime Meridian. However, it skirts around some regions and islands to prevent splitting contiguous regions and countries into two days. The world is divided into several time zones by 23 one-hour slices and two 30 minute slices. I traveled over the International Date Line from east to west, advancing the calendar by one day.

