Michigan, located in the Great Lakes region of the United States, has a rich history of railroading. The Michigan railroad map is home to several important railroads that played a crucial role in the development of its economy and transportation infrastructure. This essay provides a comprehensive guide to the railroads of Michigan, including their history, current operations, and importance to the state.
Michigan Railroad Map
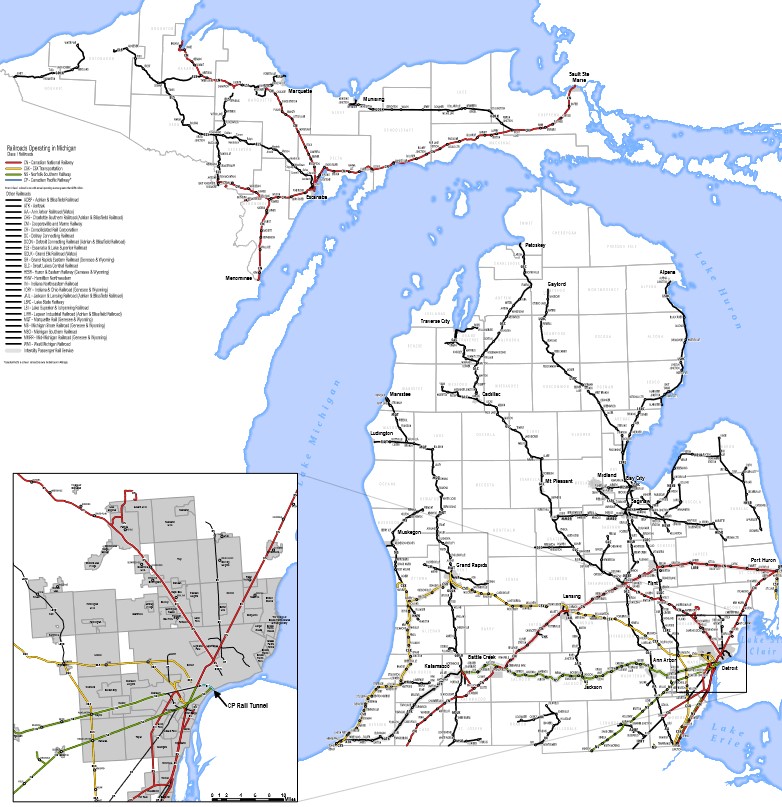
The first railroad in Michigan was the Detroit and Milwaukee Railroad, which was chartered in 1832 and began operations in 1839. This early railroad connected Detroit, Michigan to the rest of the country, making it easier to transport goods and people to and from the city. Over the next several decades, more railroads were built in Michigan, connecting major cities and towns, and supporting the state’s growing industries, such as agriculture and manufacturing.
One of the largest and most important railroads on the Michigan railroad map was the Grand Trunk Western Railroad. The Grand Trunk Western was created in 1859 as a subsidiary of the Grand Trunk Railway of Canada, and it connected several major cities in Michigan, including Detroit, Flint, and Port Huron. The railroad also connected Michigan to other states in the Great Lakes region, making it easier for goods to be transported to and from the state. The Grand Trunk Western was a major employer in Michigan, providing jobs to thousands of residents, and it played a key role in the development of the state’s economy.
Another important railroad on the Michigan railroad map was the Pere Marquette Railway. The Pere Marquette was established in 1900, and it connected several cities in Michigan, including Muskegon, Grand Rapids, and Detroit. The Pere Marquette was a significant part of Michigan’s transportation infrastructure, and it played a key role in the growth of the state’s manufacturing and agricultural industries. In 1947, the Pere Marquette was merged with several other railroads to form the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway, which continued to operate in Michigan for many years.
The Michigan Central Railroad was another major player in the state’s railroading history. The Michigan Central was established in 1848, and it connected Detroit to several other cities in Michigan and the Midwest, including Chicago, Toledo, and Buffalo. The Michigan Central was a critical part of Michigan’s transportation network, and it played a significant role in the development of the state’s economy. In the 1970s, the Michigan Central was acquired by the Canadian National Railway, which continues to operate the railroad in Michigan to this day.
In addition to these major railroads, there were also several smaller railroads that operated in the Michigan railroad map, including the Flint and Pere Marquette Railroad, the Grand Rapids and Indiana Railroad, and the Detroit, Toledo and Ironton Railroad. These smaller railroads connected cities and towns in Michigan, providing important transportation links for goods and people.
Today, the Michigan railroad map continue to play an important role in Michigan’s transportation infrastructure. The state is home to several major railroads, including the Canadian National Railway, the CSX Transportation, and the Norfolk Southern Railway. These railroads connect Michigan to other states in the Great Lakes region, and they support the state’s important industries, including agriculture, manufacturing, and shipping.
In conclusion, the Michigan railroad map provides a comprehensive overview of the railroads that have played a critical role in the development of Michigan’s economy and transportation infrastructure. From the early days of the Detroit and Milwaukee Railroad to the modern operations of major railroads like the Canadian National Railway, Michigan’s railroads have played an important role in connecting cities and towns, and supporting the state’s growing industries. Whether you’re a student of history, a railfan, or simply someone interested in Michigan’s rich railroading heritage,

